The global flexible plastic packaging market is currently experiencing a phase of stable yet increasingly differentiated growth. Starting from a market volume of USD 207.93 billion in 2024, the market is expected to expand to USD 257.58 billion by 2029. With a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.4 percent, the segment remains a core component of the global packaging industry, even though growth momentum is moderating compared to earlier expansion phases.
Growth in a Mature Market Environment
Growth is primarily driven by the food and beverage industry, which continues to represent the dominant application segment. Flexible plastic packaging stands out due to its excellent barrier properties against oxygen, moisture, and light, significantly enhancing shelf life and product safety. In light of global sustainability debates, the reduction of food waste along the supply chain is gaining additional importance. At the same time, requirements from the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors are increasing, where product protection, sterility, and traceability are critical factors.
Another structural growth driver is the continued expansion of e-commerce. The increasing direct delivery of goods to end consumers is fundamentally reshaping packaging requirements. Packaging must be mechanically robust, weight-optimized, and simultaneously suitable for branding and marketing purposes. Flexible solutions are particularly well positioned to meet these demands and therefore benefit from the digital transformation of retail and logistics.
Technological Change and Sustainability Pressure
Despite growing criticism, plastic remains the dominant material segment. Its versatility, cost efficiency, and ability to form complex multi-layer barrier structures make it indispensable for numerous applications. Nevertheless, the industry faces substantial transformation pressure. Regulatory initiatives, particularly in Europe, as well as rising societal awareness of plastic waste, are forcing manufacturers to comprehensively adjust their material strategies.
The trend is clearly moving toward recyclable mono-material structures and design-for-recycling concepts. Mechanical recycling continues to form the foundation of the circular economy but reaches technical limits when dealing with multi-layer high-barrier solutions. As a result, chemical recycling is gaining strategic importance, although its economic scalability still depends on significant investment and regulatory clarity.
At the same time, digitalization is fundamentally transforming packaging printing. Digital printing is emerging as the fastest-growing technology segment. The elimination of printing plates, reduced setup times, and the integration of variable data enable an unprecedented level of production flexibility. For brand owners, this opens new opportunities for personalization, regional differentiation, and improved traceability along the supply chain. Consequently, the printing process is increasingly becoming a strategic value driver.
Competitive Dynamics and Strategic Outlook
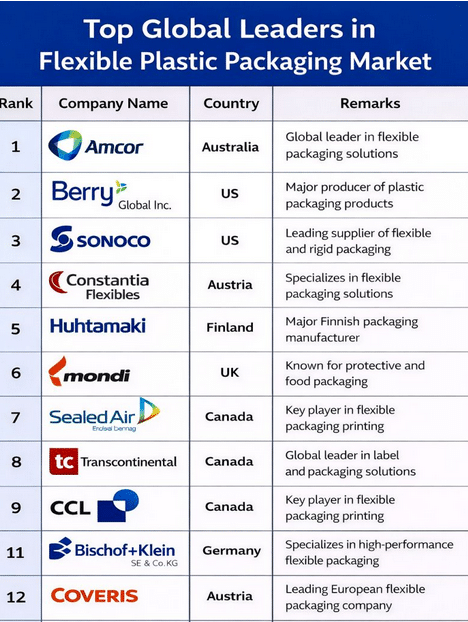
The market is characterized by pronounced consolidation dynamics. International corporations such as Amcor plc, Berry Global Inc., Sonoco Products Company, Constantia Flexibles, Huhtamaki Oyj, Mondi, Sealed Air, Transcontinental Inc., CCL Industries, Coveris, and Bischof+Klein SE & Co. KG are investing strategically in sustainable material innovations, recycling partnerships, and digital production processes. Strategic alliances along the value chain are gaining importance, as technological expertise, regulatory adaptability, and global presence increasingly determine competitive strength.
Clear regional differences are evident. North America benefits from strong innovation momentum and a dynamic e-commerce sector. Europe acts as a regulatory frontrunner with ambitious sustainability targets, while Asia-Pacific records the strongest volume growth driven by urbanization and expanding middle classes. These divergent frameworks require differentiated market strategies.
In the long term, the flexible plastic packaging market is not facing structural decline but rather a profound transformation. The functional advantages of this material class remain compelling; however, its future viability increasingly depends on the industry’s ability to reconcile environmental responsibility, technological advancement, and economic efficiency. Companies that succeed in strategically embedding this balance will play a decisive role in shaping the next phase of market development.